Periodontics focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of conditions affecting the gums and the supporting structures of teeth. One area of interest within this dental specialty is bone loss, which can occur as a result of periodontal conditions. Understanding the connection between periodontics and bone loss can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain their oral health.
What Is Bone Loss in Periodontics?
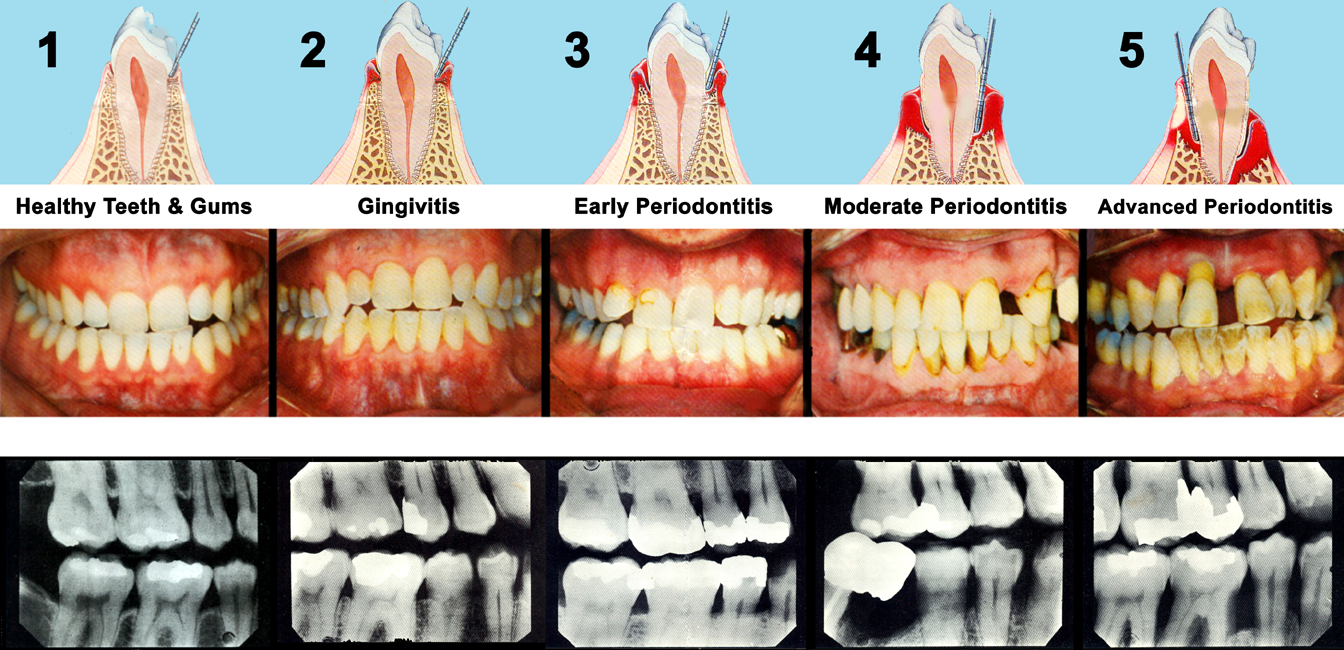
Bone loss in periodontics refers to the deterioration of the alveolar bone, which is the bone surrounding and supporting the teeth. This loss can be associated with periodontal diseases. These diseases may involve inflammation and infection of the tissues that hold the teeth in place, including the gums and the underlying bone. When untreated, bone loss can compromise the stability of teeth and may lead to further complications.
Unlike some dental conditions that are more noticeable, bone loss develops gradually. It can begin as gum inflammation, which may progress to affect deeper structures, including the connective tissue and bone. Identifying and understanding this progression can help prompt early steps for management.
What Causes Bone Loss With Periodontics?
Several factors can contribute to bone loss in relation to periodontics. These factors may include both oral health-related and systemic influences:
- Periodontal Diseases: Conditions such as gingivitis and periodontitis are leading contributors. When the gums become inflamed due to bacterial buildup, the infection can spread below the gumline, affecting the bone.
- Tooth Loss: Bone health depends on stimulation from teeth when chewing. Missing teeth can lead to reduced stimulation and gradual resorption of the alveolar bone.
- Systemic Conditions: Certain health conditions, such as diabetes and osteoporosis, may increase the likelihood of bone loss by affecting bone density and the body’s ability to recover from oral infections.
Diagnosing Bone Loss
Bone loss may be diagnosed during a periodontal evaluation. Dentists or periodontists may assess the gum tissues for signs of inflammation, measure periodontal pockets, and use X-rays to identify changes in bone levels. The presence of deep pockets between the gums and teeth is a key indicator that infection may be affecting bone structures. X-ray images can reveal the extent of bone deterioration and provide additional insights.
Managing Bone Loss
Management of bone loss may involve addressing its underlying causes, while focusing on preserving existing bone and gum structures. Treatment approaches can vary depending on the extent and severity of the condition:
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep-cleaning procedure may help to remove plaque and bacterial buildup below the gumline.
- Bone Grafting: When significant bone loss has occurred, bone grafting may be used to rebuild lost bone tissue.
- Medication: Antimicrobial treatments or medications may be prescribed to control infection and promote healing in the affected areas.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Routine cleanings and consistent oral hygiene practices are key for minimizing the risk of recurrence.
Why Does Addressing Bone Loss Matter?
When bone loss is not managed, it may lead to the loosening or loss of teeth, changes in dental alignment, or difficulties with restorative treatments. Understanding the risk factors for bone loss can play a role in maintaining overall oral function and aesthetics. While the effects of bone loss can be significant, management strategies within periodontics can provide opportunities to safeguard oral health. It can also enhance stability and help prevent future complications.
Learn More About Your Periodontal Health
If you are curious about how periodontics can support your oral health, consult with a periodontist. They are equipped to evaluate and address concerns that impact your gums and supporting structures. Whether you’re experiencing early signs of gum inflammation or seeking long-term solutions for bone loss, expert guidance can make a difference in maintaining your oral health.