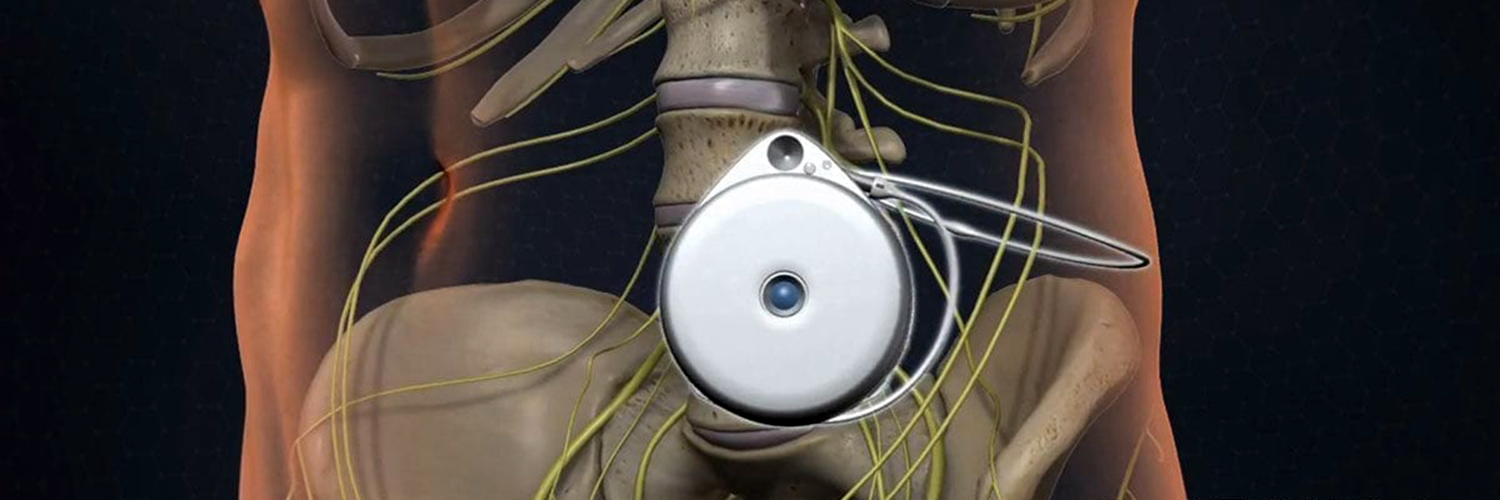
Intrathecal drug delivery is a specialized medical approach used to administer medication directly into the cerebrospinal fluid. This method allows for targeted treatment of central nervous system (CNS) disorders. By bypassing conventional pathways, it provides improved outcomes for patients with chronic pain, spasticity, and certain neurological diseases. The technique offers a promising alternative to traditional systemic drug administration, potentially revolutionizing how we manage complex CNS conditions. Its growing application in modern medicine underscores its importance.
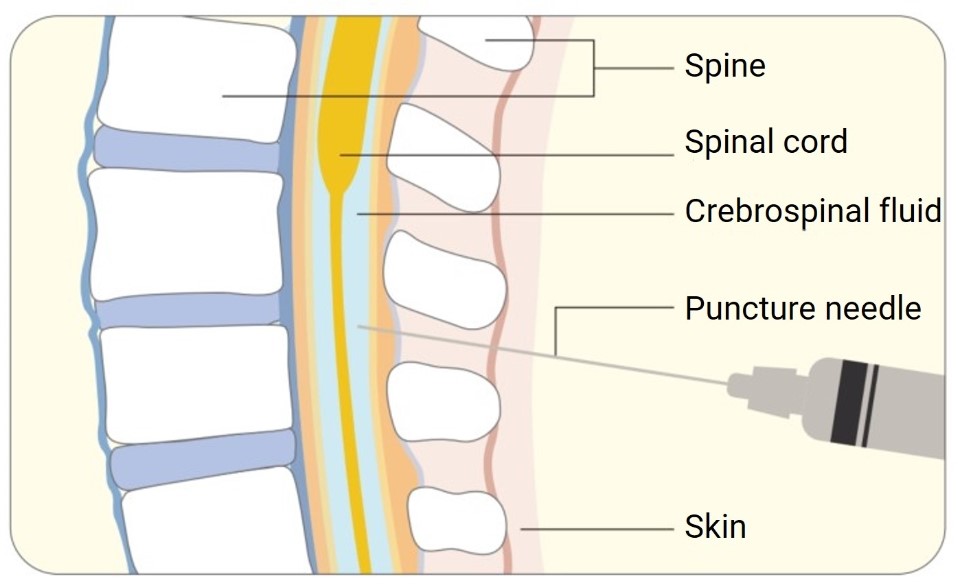
How Intrathecal Drug Delivery Works
Drug Pathway and Direct CNS Targeting
The intrathecal drug delivery method involves a precise pathway where drugs are injected directly into the cerebrospinal fluid. This injection targets the central nervous system more directly than conventional methods. Healthcare professionals achieve this by bypassing the body’s natural barriers, allowing medications to reach the intended site of action with greater efficiency. This focused approach enhances the effectiveness of drug therapy, making it particularly suitable for treating conditions within the CNS.
Role of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Delivery
The blood-brain barrier is a protective shield that prevents most drugs from entering the brain through the bloodstream. Intrathecal drug delivery circumvents this barrier, allowing medications to reach the CNS without obstruction. By delivering drugs directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, this method ensures that therapeutic agents can penetrate the CNS efficiently, leading to enhanced treatment outcomes. This is especially crucial for medications that would otherwise struggle to cross the blood-brain barrier.
Intrathecal Devices and Catheter Systems
Intrathecal drug delivery relies on specialized devices, including programmable pumps and catheter systems. Medical professionals implant these devices under the skin, typically in the lower back, to deliver medication at precise rates. The catheter is inserted into the intrathecal space, ensuring targeted delivery to the CNS. These systems offer flexibility in dosing and allow for adjustments based on therapeutic needs. They have become invaluable tools in managing chronic and complex CNS conditions.
Benefits of Intrathecal Administration
Increased Drug Potency and Lower Dosage
Intrathecal administration enhances drug potency by allowing medication to act directly on the CNS. Lower dosages become sufficient due to the direct pathway, reducing the overall amount of medication required. This precise targeting improves the therapeutic effects, making treatments more effective and efficient. As a result, patients experience better symptom management with reduced risk of overdose or drug-related complications, highlighting a key advantage of this delivery method.
Reduced Systemic Side Effects
By delivering drugs directly to the CNS, intrathecal administration minimizes systemic exposure, thereby reducing side effects commonly associated with oral or intravenous routes. This method limits medication presence in the bloodstream, decreasing the risk of adverse reactions in non-targeted body systems. Patients benefit from a more comfortable treatment experience, with fewer disruptions to their daily lives due to drug-related side effects, enhancing overall quality of life.
Enhanced Efficacy for CNS Conditions
Intrathecal administration provides enhanced efficacy in treating CNS conditions by delivering medication where it’s needed most. Diseases like chronic pain, multiple sclerosis, and spasticity respond better to this focused approach. Direct CNS targeting ensures quicker and more significant therapeutic outcomes, often surpassing the results of conventional treatments. Patients experience improved function and a higher level of symptom control, affirming the method’s effectiveness.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Chronic Pain and Spasticity Treatment
Intrathecal drug delivery is particularly effective in managing chronic pain and spasticity. It offers patients relief where traditional methods fail, allowing for better control over debilitating symptoms. The direct CNS delivery ensures potent analgesic effects and muscle relaxation, providing improved daily function and comfort. This approach is especially beneficial for patients who have not responded adequately to oral medication regimens, offering a viable long-term treatment option.
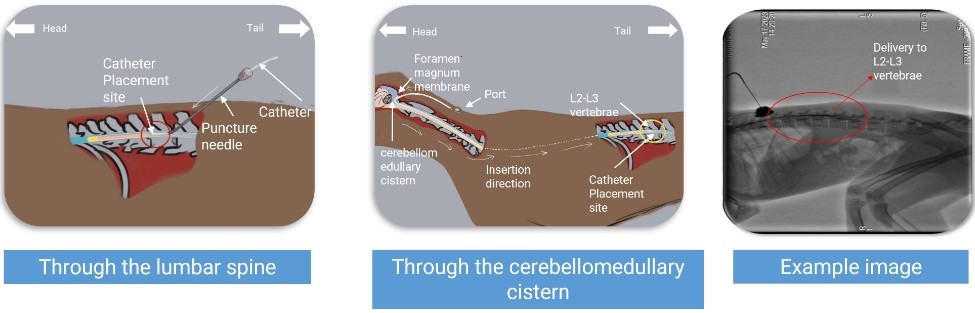
Intrathecal Chemotherapy in Cancer Care
Intrathecal delivery plays a crucial role in administering chemotherapy for certain cancers. When cancer cells invade the CNS, intrathecal chemotherapy provides targeted treatment. This method ensures high drug concentrations at the tumor site without exposing the entire body to toxic levels. By optimizing drug delivery to the brain and spinal cord, it enhances the efficacy of cancer treatment and helps prevent the spread of malignant cells, improving survival outcomes.
Emerging Uses in Neurodegenerative Disorders
Researchers are exploring intrathecal drug delivery for treating neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. This innovative approach targets disease pathways within the CNS more effectively. By delivering therapeutic agents directly to the brain, it holds potential for slowing disease progression and alleviating symptoms. The growing interest in this application reflects its promise in addressing complex neurological conditions that have limited treatment options.
Conclusion
Intrathecal drug delivery offers a groundbreaking method for treating central nervous system (CNS) disorders by allowing direct drug access to the cerebrospinal fluid. This precision enhances efficacy, minimizes systemic side effects, and improves targeting. As ongoing research uncovers new clinical applications, intrathecal delivery is emerging as a powerful tool for managing complex neurological conditions. Its ability to bypass the blood-brain barrier marks a significant advancement in modern medicine and offers hope for patients with previously untreatable diseases.